Lesson 13 Japanese Gardens
Topic Question: “Why are Japanese gardens so famous? Can you suggest one to visit?”
▮ Try Answering the Question Yourself
Think about the elements that make Japanese gardens unique and renowned worldwide. Consider suggesting a specific garden that exemplifies these characteristics.
▮ Sample Answer
“Japanese gardens are famous for their tranquility and beauty. They use natural landscapes to create peaceful spaces. The Kenrokuen Garden in Kanazawa is a great example. It’s known for its seasonal beauty, especially in autumn and spring.”
▮ Words to Learn and Their Meanings about Sample Answer
Pronounce the Words Correctly (Pronunciation Training) + Make Sentences Using the Words Instantly
- Tranquility (静けさ): Quality or state of being tranquil; calm.
- Natural landscapes (自然景観): The physical landscape or environment that has not been modified by human activity.
- Peaceful (平和な): Free from disturbance; tranquil.
- Seasonal (季節の): Relating to or varying with the seasons.
- Especially (特に): To a great extent; very much.
▮ Answer the Instructor’s Questions Based on the Sample Answer
- Why are Japanese gardens renowned?
- What makes Kenrokuen Garden worth visiting?
- In which seasons is Kenrokuen Garden particularly beautiful?
▮ Mastering Middle School English Grammar
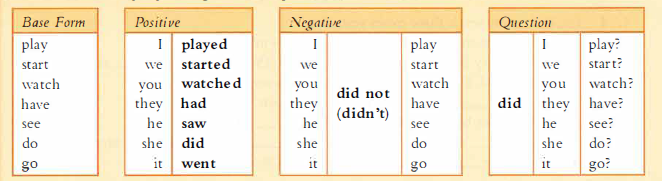
I was doing (past continuous)
A:
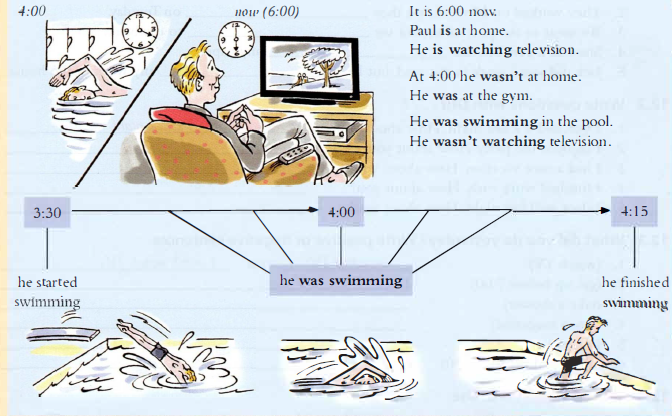
B: Was/were + -ing is the past continuous:
What were you doing at 11:30 yesterday? Were you working?
What did he say? I don’t know. I wasn’t listening.
I woke up early yesterday. It was a beautiful morning. The sun was shining, and the
birds were singing.
C: Am/is/are + -ing(present) → was/were + -ing (past):
I’ m working (now). I was working at 10:30 last night.
It isn’t raining (now). It wasn’t raining when we went out.
Example Sentences:
“What were you doing when I called you yesterday?” “I was visiting Kenrokuen Garden.”
“It was raining, but the beauty of the garden was still evident. The flowers were blooming, and the water was reflecting the sky.”
“While I was walking through the garden, I felt completely at peace.”
Make Sentences based on the above Example Sentences Yourself: